Suitable Materials
Extend the life of steel and special metalsOutstanding Wear Resistance
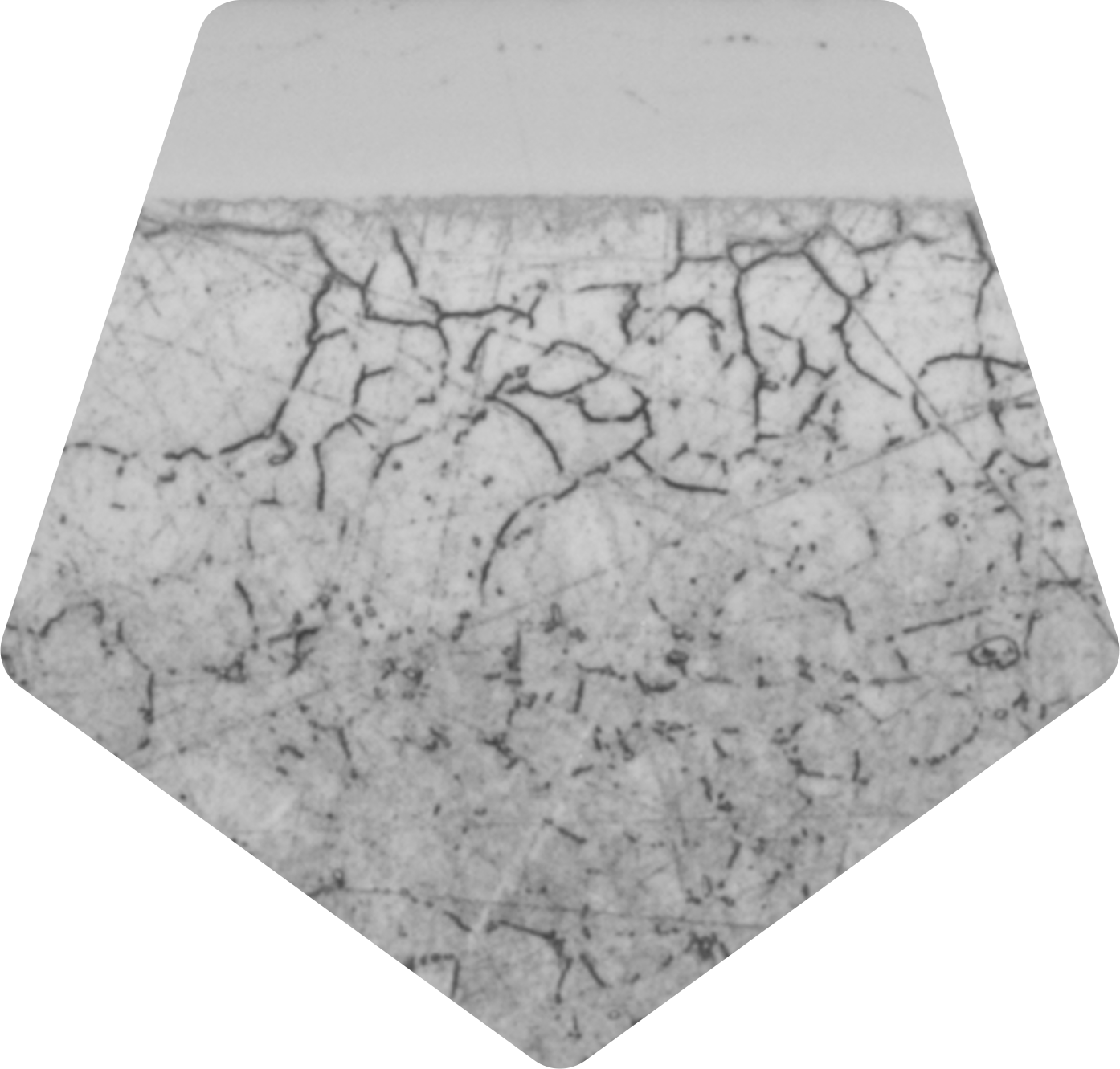
The BOROFUSE® boronizing process is carried out on a wide range of ferrous (metals containing iron) and non-ferrous materials to achieve a hardness many times higher than any other surface hardening process. Boriding of any nickel, iron or cobalt base alloy is possible. The most common materials are typically Inconel 718, Stellite 3, Tungsten Carbide (nickel or cobalt), and 1095 steel. However, a large number of other alloys have been successfully borided. MDC’s BOROFUSE process is an economical solution to a variety of demanding wear problems. Do you have a question about whether a particular material is suitable for our superior boronizing process? Please drop us a line. We’re here to help.
INCONEL & NICKEL ALLOYS
WE'VE WORKED WITH...
Hastelloy B (UNS N10001)
Hastelloy B2 (UNS N10665)
Hastelloy B3 (UNS N10675)
Hastelloy C
Hastelloy C22 (UNS N06022)
hastelloy c-276 (UNS N10276)
Hastelloy X (UNS N06002)
Inconel 200 (UNS N02200)
Inconel 600 (UNS N06600)
Inconel 625 (UNS N06625)
Inconel 686 (UNS N06686)
Inconel 718 (UNS N07718)
Inconel 725 (UNS N07725)
Inconel 800 (UNS N08810)
Inconel 825 (UNS N08825)
Inconel 925 (UNS N09925)
Inconel 945 (UNS N09945)
Inconel A-286 (UNS S66286)
Inconel X-750 (UNS N07750)
Inconel 625+ (UNS N07716)
Invar 36 (UNS K93600)
Haynes 230 (Nickel Alloy 230) (UNS N06230)
Haynes 242 (UNS N10242)
MP 35N (UNS R30035)
Nimonic 80 A (UNS N0708)
Waukesha 88 (UNS N26055)
A286 (UNS S66286)
Alloy 20 (UNS N08020)
Waspaloy (UNS N07001)
Haynes 282 (UNS N07208)
Chlorimet 3 (UNS N30107)
Ni Chrome (UNS N06003)
Hastelloy B2 (UNS N10665)
Hastelloy B3 (UNS N10675)
Hastelloy C
Hastelloy C22 (UNS N06022)
hastelloy c-276 (UNS N10276)
Hastelloy X (UNS N06002)
Inconel 200 (UNS N02200)
Inconel 600 (UNS N06600)
Inconel 625 (UNS N06625)
Inconel 686 (UNS N06686)
Inconel 718 (UNS N07718)
Inconel 725 (UNS N07725)
Inconel 800 (UNS N08810)
Inconel 825 (UNS N08825)
Inconel 925 (UNS N09925)
Inconel 945 (UNS N09945)
Inconel A-286 (UNS S66286)
Inconel X-750 (UNS N07750)
Inconel 625+ (UNS N07716)
Invar 36 (UNS K93600)
Haynes 230 (Nickel Alloy 230) (UNS N06230)
Haynes 242 (UNS N10242)
MP 35N (UNS R30035)
Nimonic 80 A (UNS N0708)
Waukesha 88 (UNS N26055)
A286 (UNS S66286)
Alloy 20 (UNS N08020)
Waspaloy (UNS N07001)
Haynes 282 (UNS N07208)
Chlorimet 3 (UNS N30107)
Ni Chrome (UNS N06003)
Nickel based alloys are excellent substrates for boriding. For Inconel 718 the inherent mechanical, corrosion and high temperature properties are perfectly compatible with the BOROFUSE process resulting in dramatic increases in the value and life of a component while maintaining the original tensile, hardness and corrosion properties. During the boriding process there are minimal changes to the microstructure of the base material as well as small changes to the dimensions. All things considered, the final properties of a BOROFUSE processed Inconel and nickel based alloys are perfectly suited for high wear demanding applications.
CEMENTED CARBIDE
WE'VE WORKED WITH...
Tungsten Carbide (Cobalt Binder)
Tungsten Carbide (Nickel Binder)
Tungsten Carbide (Nickel Binder)
Tungsten carbide with a nickel or cobalt binder has a very high hardness. The strength results from the extremely hard tungsten carbide particles bonded together using cobalt or nickel alloys. Specific properties can be achieved by varying the percent of binder, type and the particle size. Lowering the binder percent results in a trade-off between hardness and brittleness; boriding cemented carbide allows the best of both. By boriding a higher percent binder we can maintain tough core properties but increases the binder hardness at the surface up to the hardness of the carbide particles. This dramatically increases the wear resistance without increasing the brittleness of the core. BOROFUSE enables the use of more commercially available tungsten carbide while attaining lower wear rates than more expensive alternatives.
STEEL & IRON ALLOYS

WE'VE WORKED WITH...
9% Chrome (UNS S50400)
AISI 4130 (UNS G41300)
AISI 4142 (UNS G41420)
AISI 4150 (UNS G41500)
AISI 4320 (UNS G43200)
AISI 4340 (UNS G43400)
AISI 4620 (UNS G46200)
AISI 52100 (UNS G52986)
AISI 6145 (UNS G61450)
AISI 6150 (UNS G61500)
AISI 8620 (UNS G86200)
AISI 8650 (UNS G86500)
AISI 9310 (UNS G93100)
F22 (UNS K21590)
F5 (UNS K41545)
Kromite #3
P-5 (UNS K41545)
Ni-Resist (UNS F41000)
AISI 302 (UNS S30200)
AISI 303 (UNS S30300)
AISI 304 (UNS S30400)
AISI 316 (UNS S31600)
AISI 347 (UNS S34700)
Nitronic 50 (XM-19) (UNS S20910)
M-50 (UNS K88165)
AISI 1012 (UNS G10120)
AISI 1018 (UNS G10180)
AISI 1020 (UNS G10200)
AISI 1022 (UNS G10220)
AISI 1060 (UNS G10600)
AISI 1095 (UNS G10950)
AISI 1137 (UNS G11370)
AISI 1144 (UNS G11440)
C20
AISI 1021 (UNS G10210)
316 Cast (UNS J92900)
ABEX-HC-250
Durcomet 100
Ferralium 255 (UNS S32550)
SA-182 (UNS S32205)
Iron (UNS K93602)
AISI 400 (UNS N04400)
AISI 430 (UNS S43000)
AISI 444 (UNS S44400)
Kovar (Alloy 2917, Rodar Alloy) (UNS K94610)
ASP23
BG 42 (UNS S42700)
Bohler S705 (UNS T11341)
M-1 (UNS T11301)
M-2 (UNS T11302)
M-3 (UNS T11313)
M-4 (UNS T11304)
M-7 (UNS T11302)
T-1 (UNS T12001)
T-15 (UNS T12015)
T-4 (UNS T12004)
H-13 (UNS T20813)
AISI 4140 (UNS G41400)
Nitralloy 135 (UNS K24065)
P-20 (UNS T51620)
P-21 (UNS T51621)
Maraging 300 (Vascomax 300) (UNS K93120)
Maraging 350 (Vascomax 350) (UNS S35000)
AISI 410 (UNS S41000)
AISI 416 (UNS S41600)
AISI 420 (UNS S42000)
AISI 421 (UNS S42100)
AISI 422 (UNS S42200)
AISI 440C (UNS S44004)
AISI 455 (UNS S45500)
AISI 465 (UNS s46500)
Vasco Greek Ascoloy (UNS S41800)
15-5 (UNS S15500)
17-4 (UNS S17400)
17-7 (UNS S17700)
AL6XN (UNS N08367)
A-10 (UNS T30110)
A-11 (CPM10V) (UNS T30311)
A-2 (UNS T30102)
A-4 (UNS T30104)
A-6 (UNS T30106)
A-7 (UNS T30107)
A-8 (UNS T30108)
CPM10V (A-11) (UNS T30311)
CPM15V
CPM3V
CPM9V
CRU-WEAR (Vasco-Wear)
D-2 (UNS T30402)
D-4 (UNS 30404)
D-7 (UNS T30407)
L-6 (UNS T61206)
M-42 (UNS T11342)
O-1 (UNS T31501)
S-5 (UNS T41905)
S-6 (UNS T41906)
S-7 (UNS T41907)
Hi Chrome (White Iron)
Duriron
AISI 4130 (UNS G41300)
AISI 4142 (UNS G41420)
AISI 4150 (UNS G41500)
AISI 4320 (UNS G43200)
AISI 4340 (UNS G43400)
AISI 4620 (UNS G46200)
AISI 52100 (UNS G52986)
AISI 6145 (UNS G61450)
AISI 6150 (UNS G61500)
AISI 8620 (UNS G86200)
AISI 8650 (UNS G86500)
AISI 9310 (UNS G93100)
F22 (UNS K21590)
F5 (UNS K41545)
Kromite #3
P-5 (UNS K41545)
Ni-Resist (UNS F41000)
AISI 302 (UNS S30200)
AISI 303 (UNS S30300)
AISI 304 (UNS S30400)
AISI 316 (UNS S31600)
AISI 347 (UNS S34700)
Nitronic 50 (XM-19) (UNS S20910)
M-50 (UNS K88165)
AISI 1012 (UNS G10120)
AISI 1018 (UNS G10180)
AISI 1020 (UNS G10200)
AISI 1022 (UNS G10220)
AISI 1060 (UNS G10600)
AISI 1095 (UNS G10950)
AISI 1137 (UNS G11370)
AISI 1144 (UNS G11440)
C20
AISI 1021 (UNS G10210)
316 Cast (UNS J92900)
ABEX-HC-250
Durcomet 100
Ferralium 255 (UNS S32550)
SA-182 (UNS S32205)
Iron (UNS K93602)
AISI 400 (UNS N04400)
AISI 430 (UNS S43000)
AISI 444 (UNS S44400)
Kovar (Alloy 2917, Rodar Alloy) (UNS K94610)
ASP23
BG 42 (UNS S42700)
Bohler S705 (UNS T11341)
M-1 (UNS T11301)
M-2 (UNS T11302)
M-3 (UNS T11313)
M-4 (UNS T11304)
M-7 (UNS T11302)
T-1 (UNS T12001)
T-15 (UNS T12015)
T-4 (UNS T12004)
H-13 (UNS T20813)
AISI 4140 (UNS G41400)
Nitralloy 135 (UNS K24065)
P-20 (UNS T51620)
P-21 (UNS T51621)
Maraging 300 (Vascomax 300) (UNS K93120)
Maraging 350 (Vascomax 350) (UNS S35000)
AISI 410 (UNS S41000)
AISI 416 (UNS S41600)
AISI 420 (UNS S42000)
AISI 421 (UNS S42100)
AISI 422 (UNS S42200)
AISI 440C (UNS S44004)
AISI 455 (UNS S45500)
AISI 465 (UNS s46500)
Vasco Greek Ascoloy (UNS S41800)
15-5 (UNS S15500)
17-4 (UNS S17400)
17-7 (UNS S17700)
AL6XN (UNS N08367)
A-10 (UNS T30110)
A-11 (CPM10V) (UNS T30311)
A-2 (UNS T30102)
A-4 (UNS T30104)
A-6 (UNS T30106)
A-7 (UNS T30107)
A-8 (UNS T30108)
CPM10V (A-11) (UNS T30311)
CPM15V
CPM3V
CPM9V
CRU-WEAR (Vasco-Wear)
D-2 (UNS T30402)
D-4 (UNS 30404)
D-7 (UNS T30407)
L-6 (UNS T61206)
M-42 (UNS T11342)
O-1 (UNS T31501)
S-5 (UNS T41905)
S-6 (UNS T41906)
S-7 (UNS T41907)
Hi Chrome (White Iron)
Duriron
An extremely wide range of iron based alloys are viable substrates for the BOROFUSE process. Iron based materials were some of the first alloys that were commercially borided. Air hardened steels have been very successfully borided resulting in the very hard surface with a fully hardened substrate. Borided iron based alloys can have excellent friction and wear improvement over un-borided components, which can lead to extensive improvements in part life.
COBALT BASED ALLOYS

WE'VE WORKED WITH...
Ultimet Cobalt Based (UNS R31233)
Haynes 25 (Stellite 25) (UNS R30605)
Stellite 3 (UNS R30103)
Stellite 31 (UNS R30031)
Stellite 6 (UNS R30006)
Stellite 6B (UNS R30016)
Haynes 25 (Stellite 25) (UNS R30605)
Stellite 3 (UNS R30103)
Stellite 31 (UNS R30031)
Stellite 6 (UNS R30006)
Stellite 6B (UNS R30016)
Boriding cobalt based alloys is similar to nickel based alloys. The substrate maintains the core properties while selectively hardening the surface. While many cobalt based alloys have excellent wear and erosion properties, which can be significantly improved through boriding to meet the requirements for the harshest environments. Cobalt based alloys are also very stable through the thermochemical process.
